一线产区的优势
一线产区因其独特的地理位置和气候条件,通常具备更高质量的农产品。这些地区往往拥有丰富的自然资源,例如优质水源、充足阳光及肥沃土壤,这些因素共同作用,使得作物生长更加健康。生产过程中,小规模家庭农业与现代化大规模种植相结合,提高了生产效率,并确保了品质稳定。
技术研发推动发展
技术创新在一线产区尤为显著。从精细化管理到智能农业,一系列先进技术被广泛应用。这不仅提高了耕作效率,还减少了环境影响。例如,通过精准施肥和病虫害监测,能够最大限度地利用资源,同时降低成本。此外,大数据分析也使得农民能根据市场需求及时调整种植策略,从而提升收益。
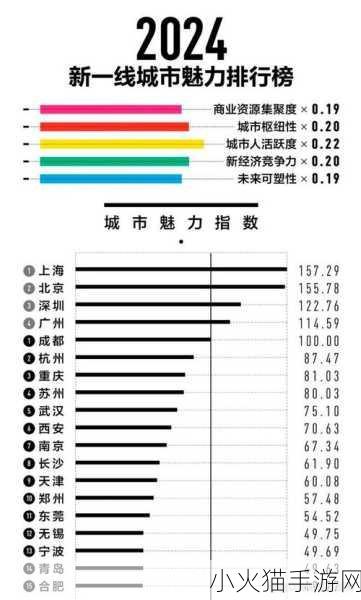
品牌效应及市场认知
品牌塑造对于一线产区来说是另一项重要因素。长期以来,这些地区通过积极营销建立起良好的口碑,消费者对其产品产生信任感。因此,在购买决策中,他们愿意为这些信誉卓越的品牌支付溢价。而二线产区由于缺乏这样的宣传与推广,很难获得同样程度的认可,这直接影响了销售额和利润空间。
政策支持的重要性
The government plays a crucial role in shaping the agricultural landscape. 一线产区通常享受到更多政策优惠,包括财政补贴、税收减免以及基础设施建设等方面支持。这类措施帮助他们不断改善运营模式,提高竞争力。而在一些二线产区,由于资金短缺或政务透明度不足,经常面临发展的限制。他们所需的发展手段往往无法得到有效保障,从而妨碍整体进步。
人才储备差距明显
A higher concentration of educational institutions and研究中心 exists in first-tier regions, leading to a more qualified workforce for agriculture-related industries. 这种专业知识不仅有助于提高日常操作水平,也促进新思想、新方法在产业中的落地实施。然而,许多二-line districts lack such resources, resulting in talent shortages that hinder their growth.
供应链体系完善程度不同
Sophisticated supply chain systems are another key differentiator between first- and second-tier production areas. One line areas often benefit from developed logistics networks which ensure timely distribution of products to markets. This reduces spoilage rates and helps maintain product freshness, ultimately driving up sales potential. In contrast, many second-line areas face logistical challenges that can lead to delays or increased costs, affecting overall market competitiveness.
User Needs: Exploring Market Trends Further!
- The impact of climate change on agricultural output across different tiers.
- The importance of sustainable practices in food production.
- An analysis of consumer preferences towards locally sourced versus imported goods.